2.5. PION setup for AGN warm absorber¶
By: Junjie Mao, Missagh Mehdipour, and Jelle Kaastra
2.5.1. Goal¶
Setup the PION model for the warm absorber in a nearby Seyfert 1 galaxy observed with Chandra HRC/LETGS.
Note
A simulated spectrum was used because this thread merely intends to show the setup of the PION model.
2.5.2. Preparation¶
To follow this thread, you need to download the example files here: chl.spo and
chl.res.
2.5.3. Start SPEX¶
Start SPEX in a linux terminal window:
user@linux:~> spex
Welcome user to SPEX version 3.05.00
SPEX>
2.5.4. Load data¶
A command file tailored for this thread to load data is available here data.com
user@linux:~> cat data.com
# Simulated data
#---------------
# HRC/LETGS DATA
data chl chl
bin inst 1 reg 1 0:10000 2 unit ang
ignore inst 1 reg 1 0:1.5 unit ang
ignore inst 1 reg 1 60:1000 unit ang
Load the above command file into SPEX:
SPEX> log exe data
2.5.5. Plot data¶
A command file tailored for this thread to plot the data is available here plot.com
user@linux:~> cat plot.com
# plot setting
plot dev xw
plot type data
plot x lin
plot ux a
plot rx 1.5:60
plot y lin
plot uy fa
plot ry 0:20
plot set 1
plot mo lw 3
plot fill disp f
plot back disp f
plot cap id disp f
plot cap ut disp f
plot cap lt disp f
plot
Load the above command file into SPEX:
SPEX> log exe plot
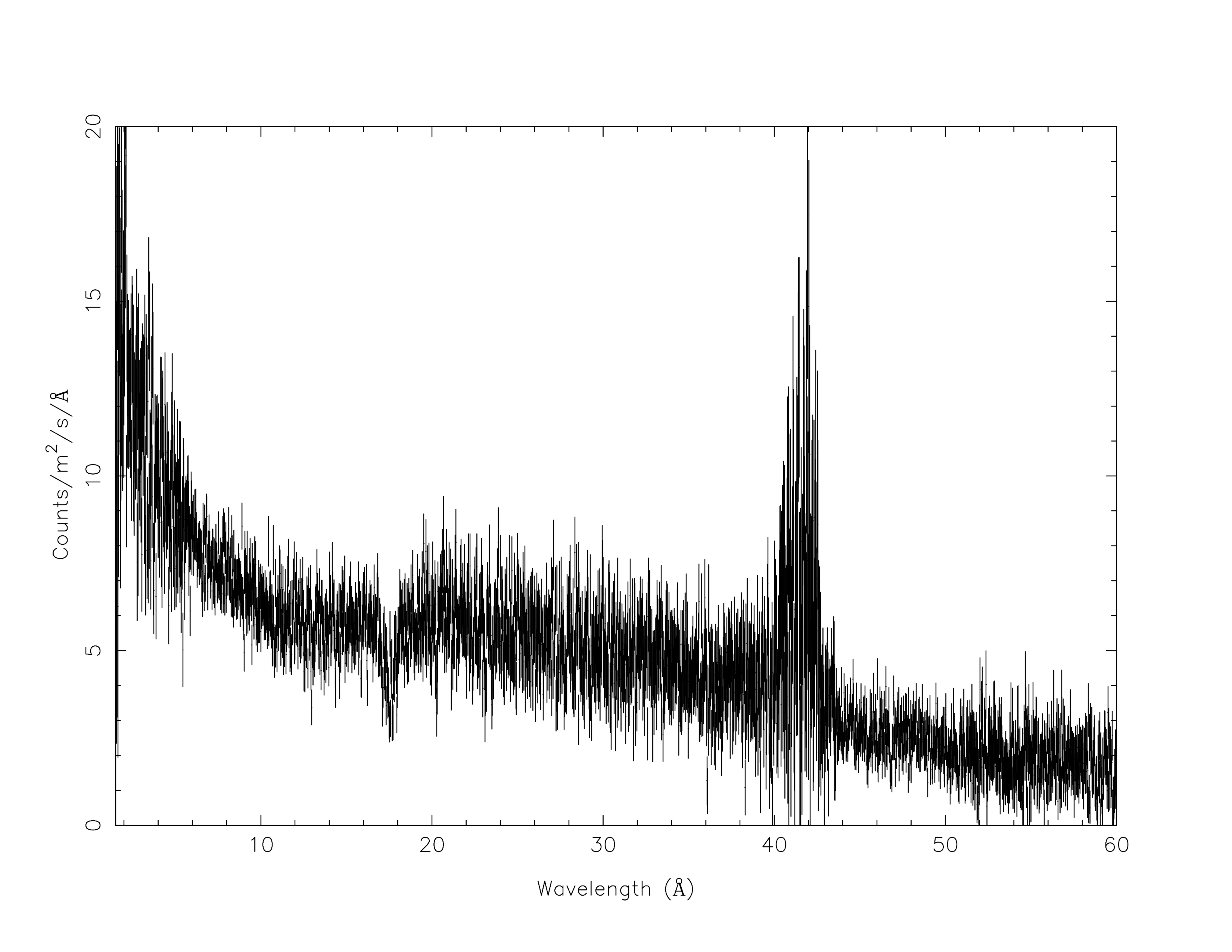
2.5.6. Define model components and component relations (step-by-step)¶
Here we are looking at the warm absorber in a nearby (z = 0.07) Seyfert 1 galaxy.
2.5.6.1. Set the distance of the source¶
SPEX> dist 0.07 z
Distances assuming H0 = 70.0 km/s/Mpc, Omega_m = 0.300 Omega_Lambda = 0.700 Omega_r = 0.000
Sector m A.U. ly pc kpc Mpc redshift cz age(yr)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 9.740E+24 6.511E+13 1.030E+09 3.157E+08 3.157E+05 315.6554 0.0700 20985.5 9.302E+08
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SPEX> com reds
You have defined 1 component.
SPEX> par 1 1 z val 0.07
2.5.6.2. Set the redshift component¶
SPEX> com reds
You have defined 1 component.
SPEX> par 1 1 z val 0.07
2.5.6.3. Set the galactic absorption¶
SPEX> com hot
You have defined 2 components.
SPEX> par 1 2 nh val 2.0e-4
SPEX> par 1 2 t val 8E-6
SPEX> par 1 2 t s f
SPEX> par 1 2 nh s f
2.5.6.4. Set the SED¶
Set the intrinsic spectral-energy-distribution (SED) of the AGN above the Lyman limit along our line-of-sight.
- For a typical Seyfert 1 galaxy, the SED has three components (Mehdipour et al. 2015):
A Comptonized disk component (Comt: comptonisation model) for optical to soft X-rays data,
A power-law component (Pow: power law model) for X-ray data,
A neutral reflection component (Refl: reflection model) for hard X-rays data. Usually, the reflection component has an exponential cut-off energy (300 keV here).
SPEX> com comt
You have defined 3 components.
SPEX> par 1 3 norm val 3.E12
SPEX> par 1 3 norm s f
SPEX> par 1 3 t0 val 5e-4
SPEX> par 1 3 t0 s f
SPEX> par 1 3 t1 val 0.15
SPEX> par 1 3 t1 s f
SPEX> par 1 3 tau val 20
SPEX> par 1 3 tau s f
SPEX> com pow
You have defined 4 components.
SPEX> par 1 4 norm val 1.E+09
SPEX> par 1 4 norm s t
SPEX> par 1 4 gamm val 1.7
SPEX> par 1 4 gamm s t
SPEX> com refl
You have defined 5 components.
SPEX> par 1 5 norm couple 1 4 norm
SPEX> par 1 5 gamm couple 1 4 gamm
SPEX> par 1 5 ecut val 300
SPEX> par 1 5 ecut s f
SPEX> par 1 5 pow:fgr v 0
SPEX> par 1 5 scal val 1.
SPEX> par 1 5 scal s f
2.5.6.5. Apply an exponential cut-off to the power-law¶
Apply exponential cut-off to the power-law component of the SED both below the Lyman limit and above the high-energy cut-off.
Note
The ecut parameter in the refl component applies to itself only.
SPEX> com etau
You have defined 6 components.
SPEX> par 1 6 a val -1
SPEX> par 1 6 a s f
SPEX> par 1 6 tau val 1.3605E-2
SPEX> par 1 6 tau s f
SPEX> com etau
You have defined 7 components.
SPEX> par 1 7 a val 1
SPEX> par 1 7 a s f
SPEX> par 1 7 tau val 3.3333E-3
SPEX> par 1 7 tau s f
2.5.6.6. Set the PION (absorption) components¶
Here we introduce three PION components (Pion: SPEX photoionised plasma model). The parameters of the PION components are restricted to
improve the efficiency of a realistic fitting process. fcov=1 refers to the PION component fully covers the
line-of-sight. omeg=1.E-7 refers to a negligible solid angle () subtended by the PION component
with respect to the nucleus (omeg =
).
Note
The third pion component is a spare one with fcov=0 and omeg=0. This is practical when analyzing
real data without any prior knowledge of the number of PION components required.
Note
To see the density effect of the absorption features, it is necessary to set a non-zero omeg value.
SPEX> com pion
You have defined 8 components.
** Pion model: take care about proper COM REL use: check manual!
SPEX> com pion
You have defined 9 components.
** Pion model: take care about proper COM REL use: check manual!
SPEX> com pion
You have defined 10 components.
** Pion model: take care about proper COM REL use: check manual!
SPEX> par 1 8:10 nh range 1.E-7:1.E1
SPEX> par 1 8:10 xil range -5:5
SPEX> par 1 8:10 omeg range 0:1
SPEX> par 1 8 nh val 5.E-03
SPEX> par 1 8 xil val 2.7
SPEX> par 1 8 zv val -500
SPEX> par 1 8 zv s t
SPEX> par 1 8 v val 100
SPEX> par 1 8 v s t
SPEX> par 1 8 omeg val 1.E-7
SPEX> par 1 9 nh val 2.E-03
SPEX> par 1 9 xil val 1.6
SPEX> par 1 9 zv val -100
SPEX> par 1 9 zv s t
SPEX> par 1 9 v val 50
SPEX> par 1 9 v s t
SPEX> par 1 9 omeg val 1.E-7
SPEX> par 1 10 nh val 1.E-7
SPEX> par 1 10 xil val 0
SPEX> par 1 10 fcov val 0
SPEX> par 1 10 omega val 0
2.5.6.7. Set component relation along our line of sight¶
Set the component relation for the intrinsic AGN SED above the Lyman limit along our line-of-sight.
Note
Photons from both the Comptonized disk and power-law components are screened by the warm absorber components at the redshift of the target, as well as the galactic absorption before reaching the detector. Photons from the neutral reflection component is assumed not to be screened by the warm absorber for simplicity. It is still redshifted and requires the galactic absorption.
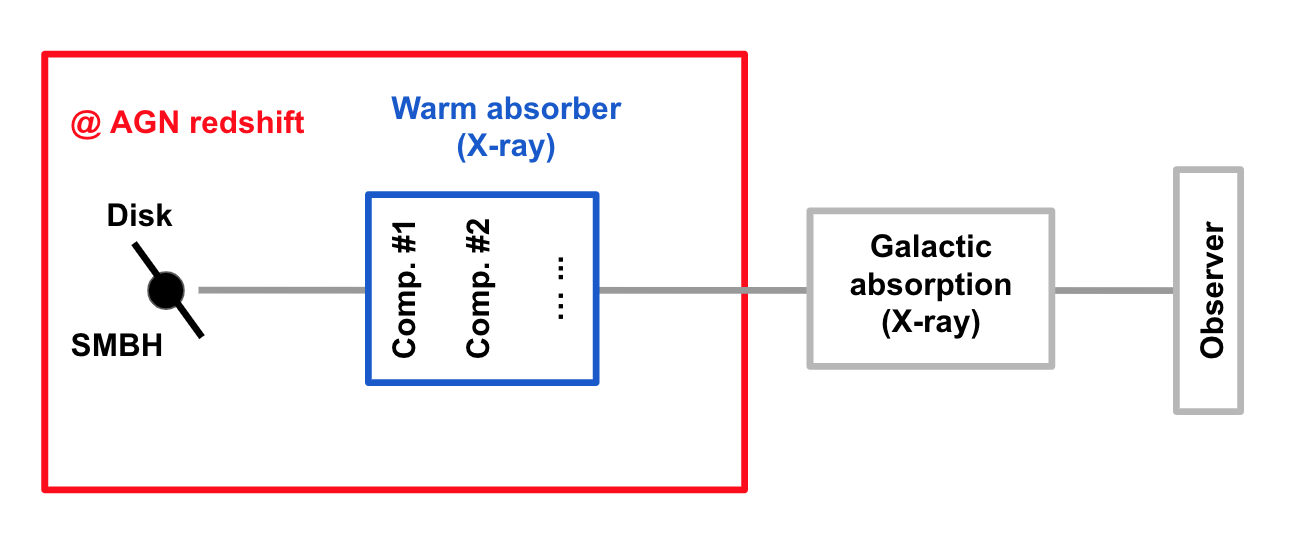
SPEX> com rel 3 8,9,10,1,2
SPEX> com rel 4 6,7,8,9,10,1,2
SPEX> com rel 5 1,2
2.5.6.8. Set the component relation for the PION components¶
Assuming that the warm absorber components closer to the central engine are defined first (with a smaller component
index), photons transmitted from the inner PION components (with a nonzero omeg value) are screened by all the
outer PION components at the redshift of the target, as well as the galactic absorption before reaching the detector:
SPEX> com rel 8 9,10,1,2
SPEX> com rel 9 10,1,2
SPEX> com rel 10 1,2
2.5.6.9. Check the model settings and calculate¶
We check the setting of the component relation:
SPEX> model show
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of sectors : 1
Sector: 1 Number of model components: 10
Nr. 1: reds
Nr. 2: hot
Nr. 3: comt[8,9,10,1,2 ]
Nr. 4: pow [6,7,8,9,10,1,2 ]
Nr. 5: refl[1,2 ]
Nr. 6: etau
Nr. 7: etau
Nr. 8: pion[9,10,1,2 ]
Nr. 9: pion[10,1,2 ]
Nr. 10: pion[1,2 ]
We check the setting of the free parameters and calculate the 1–1000 Ryd ionizing luminosity:
SPEX> elim 1.E0:1.E3 ryd
SPEX> calc
SPEX> plot
SPEX> par show free
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sect comp mod acro parameter with unit value status minimum maximum lsec lcom lpar
1 3 comt norm Norm (1E44 ph/s/keV) 3.0000001E+12 thawn 0.0 1.00E+20
1 3 comt t0 Wien temp (keV) 5.0000002E-04 thawn 1.00E-05 1.00E+10
1 3 comt t1 Plasma temp (keV) 0.1500000 thawn 1.00E-05 1.00E+10
1 3 comt tau Optical depth 20.00000 thawn 1.00E-03 1.00E+03
1 4 pow norm Norm (1E44 ph/s/keV) 1.0000000E+09 thawn 0.0 1.00E+20
1 4 pow gamm Photon index 1.700000 thawn -10. 10.
1 8 pion nh X-Column (1E28/m**2) 4.9999999E-03 thawn 1.00E-07 10.
1 8 pion xil Log xi (1E-9 Wm) 2.700000 thawn -5.0 5.0
1 8 pion v RMS Velocity (km/s) 100.0000 thawn 0.0 3.00E+05
1 8 pion zv Average vel. (km/s) -500.0000 thawn -1.00E+05 1.00E+05
1 9 pion nh X-Column (1E28/m**2) 2.0000001E-03 thawn 1.00E-07 10.
1 9 pion xil Log xi (1E-9 Wm) 1.600000 thawn -5.0 5.0
1 9 pion v RMS Velocity (km/s) 50.00000 thawn 0.0 3.00E+05
1 9 pion zv Average vel. (km/s) -100.0000 thawn -1.00E+05 1.00E+05
Instrument 1 region 1 has norm 1.00000E+00 and is frozen
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Fluxes and restframe luminosities between 1.36057E-02 and 13.606 keV
sect comp mod photon flux energy flux nr of photons luminosity
(phot/m**2/s) (W/m**2) (photons/s) (W)
1 3 comt 9.90871 4.310500E-16 1.447224E+54 7.988849E+36
1 4 pow 243.883 6.246949E-14 2.869709E+54 1.021577E+38
1 5 refl 5.98565 7.190691E-15 6.284842E+51 7.467485E+36
1 8 pion 1.711172E-07 3.011339E-23 3.540241E+45 8.248552E+28
1 9 pion 1.753678E-06 1.559744E-22 1.947966E+47 1.168208E+30
1 10 pion 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000
Fit method : Classical Levenberg-Marquardt
Fit statistic : C-statistic
C-statistic : 2424.54
Expected C-stat : 2348.67 +/- 68.66
Chi-squared value : 2531.73
Degrees of freedom: 0
W-statistic : 2353.74
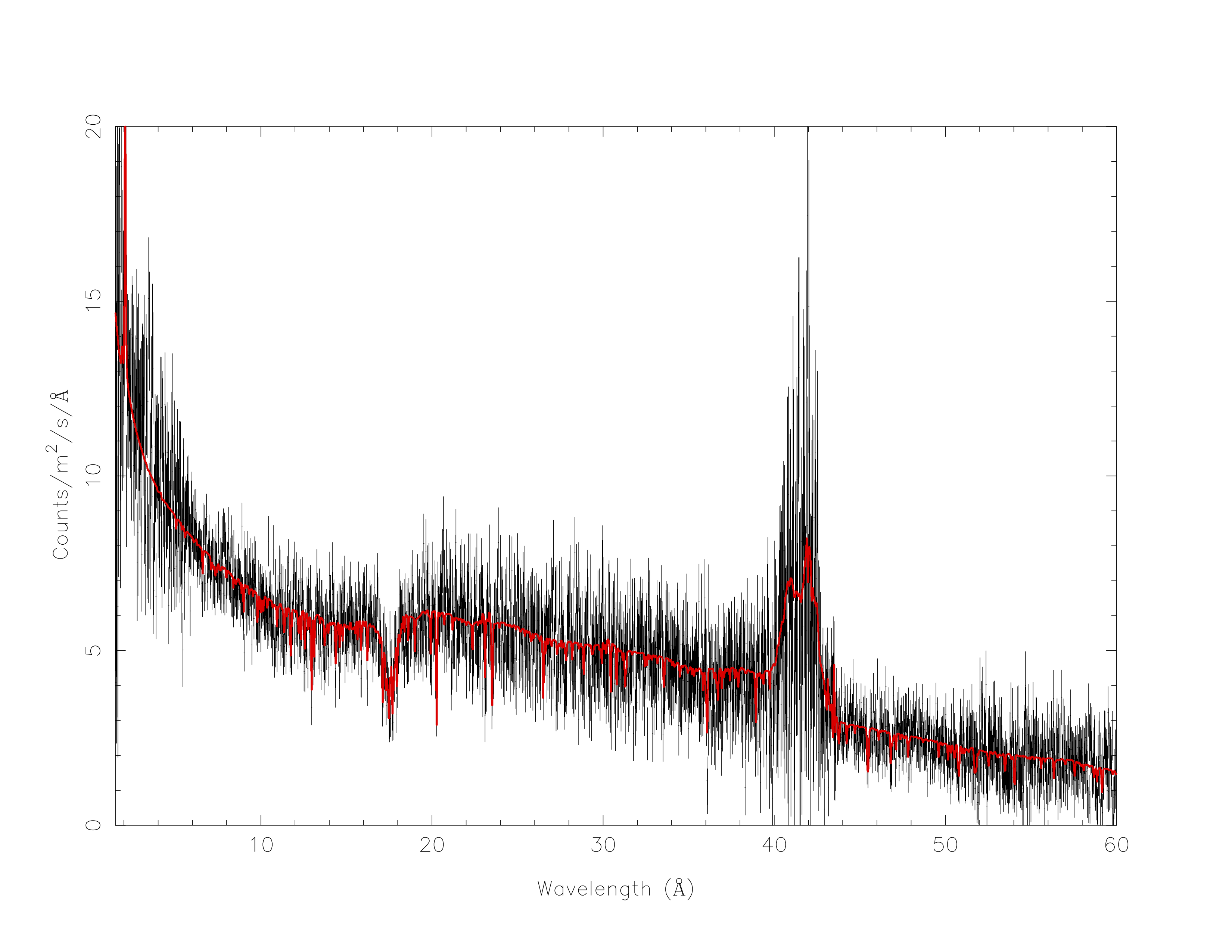
2.5.7. Final remarks¶
This is the end of this analysis thread. If you want, you can quit SPEX now:
SPEX> quit
Thank you for using SPEX!
Below, we provide a useful command file.
2.5.7.1. Define model components and component relations (running scripts)¶
A command file tailored for this thread to setup the model components and parameters is available
here mdl_pa.com.
Load the above command file into SPEX:
SPEX> log exe mdl_pa
